A Study of the Threes Phenomena
| Nature of 3s... 1 | Nature of 3s... 2 | Nature of 3s... 3 | Nature of 3s... 2 |
Viewers since August 9th, 2025
Permit me to momentarily digress from the previous page to make some explanatory comments:
Yes, there are multiple other patterns humans can perceive than the "three" being expressed in different forms. For example, someone told me that they have a preference for the number 7, I told them that I too would think the number 7 as important...
- if we lived on the 7th planet instead of the 3rd,
- if there were 7 fundamental particles instead of 3 (Protons-Neutrons-Electrons),
- if there were 7 families of fundamental particles instead of 3,
- if DNA had a 7-code instead of a triplet,
- if there were 7 Germ layers instead of 3,
- if there were 7 basic sources for cellular energy instead of 3 (AMP-ADP-ATP),
- if most people held a pen, pencil, paintbrush with 7 fingers instead of 3,
- if the word order of languages focused on 7 distinctions instead of 3,
- if there were 7 traditional social classes instead of 3,
- if human pregnancy was divided into 7 instead of 3 trimesters,
- if there were 7 eye cones for color instead of 3,
- if there were 7 major University degrees instead of 3 (PhD-Master's-Bachelors),
- if baseball had 7 strikes instead of 3,
- if a plane made a 7-point landing instead of 3,
- if there were 7 coin combinations for vending machines instead of 3,
- if there were 7 traditional human races instead of 3 (Asian-African-Caucasian),
- if basketball had a 7 point shot instead of 3,
- if there were 7 items to a fast-food combo-meal instead of 3 (drink- sandwich- side order),
- if there were 7 Olympic medals instead of 3 (gold- silver- bronze),
- if water had 7 atoms instead of 3 (2 Hydrogen, 1 Oxygen),
- if a 7 -to- 1 ratio was more prevalent than a 3 -to- 1 ratio,
- etc...
The following examples of "7" ideas comes from here: Things that come in Sevens. In a few cases I had to look up the exact examples to include them and let me also add one of my own that is not to be found anywhere even though it is obvious concerning the teenage years:
7 TEENAGE YEARS:
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
And here is yet another usage of the "7" theme by one or more writers who don't back up their report but for some reason we continue to find people using the number as if it's presence in a report has some sort of ability to lend authenticity: "It’s believed that, even as you read this news story, there is around 7 credit cards worth of plastic circulating in your body." (Source: There's a surprising easy way to remove microplastics from drinking water: Boil it, by Anthony Corbley, Aug. 11th, 2024)
- 7 seas:
- North Atlantic Ocean
- South Atlantic Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- North Pacific Ocean
- South Pacific Ocean
- Arctic Ocean
- Southern Ocean (or Antarctic Ocean)
- 7 days of the week:
- Sunday
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- 7 continents:
- Africa
- Antarctica
- Asia
- Australia
- Europe
- North America
- South America
- 7 colors of the rainbow:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
- 7 Deadly Sins:
- Lust
- Gluttony
- Greed
- Sloth
- Wrath
- Envy
- Pride
- 7 Hills of Rome:
- Aventine Hill
- Caelian Hill
- Capitoline Hill
- Esquiline Hill
- Palatine Hill
- Quirinal Hill
- Viminal Hill
- 7 Present day wonders:
- Great Wall of China
- Petra
- Christ the Redeemer
- Machu Picchu
- Chichén Itzá
- Roman Colosseum
- Taj Mahal
- 7 Ancient wonders:
- Great Pyramid of Giza
- Hanging Gardens of Babylon
- Statue of Zeus at Olympia
- Temple of Artemis at Ephesus
- Mausoleum at Halicarnassus
- Colossus of Rhodes
- Lighthouse of Alexandria
- 7 Western Music notes:
- C: Also known as the “tonic,” it serves as the fundamental note of a musical piece.
- D: The second note, creating a whole tone or two half steps above the tonic.
- E: The third note, another whole tone above the second note.
- F: The fourth note, a half step above the third note.
- G: The fifth note, creating a whole tone above the fourth note.
- A: The sixth note, forming a whole tone above the fifth note.
- B: The 7th note, a whole tone above the sixth note.
- 7 days of creation: (7 creation days)
- 1st day- God creates the heavens and the earth.
- 2nd day- God creates the sky.
- 3rd day- God creates dry land.
- 4th day- God creates all the stars and heavenly bodies.
- 5th day- God creates all life that lives in the water, and also makes all the birds.
- 6th day- God creates all the creatures that live on dry land.
- 7th day- God rests. (It is said that this all powerful god got weary.)
- 7 Virtues:
- Chastity
- Temperance
- Charity
- Diligence
- Patience
- Kindness
- Humility
- 7 stages of Economic Production:
- Extraction
- Production
- Distribution
- Marketing
- Retail
- Consumption
- Post-Consumption
- 7 dwarfs from various cultural sources:
- Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs: (7 dwarfs names)
- Doc
- Sleepy
- Dopey
- Grumpy
- Happy
- Bashful
- Sneezy
- Norse Mythology: (no specific group, primarily referencing the 7 of German fairy tale Snow White.)
- Tolkien’s Middle-earth:
- Durin's Folk - The most prominent house, known for their lineage from Durin the Deathless.
- House of Grey Mountains - Dwarves from the Grey Mountains, known for their resilience.
- House of the Iron Hills - Renowned for their mining and metalwork skills.
- House of the Blue Mountains - Dwarves who settled in the Blue Mountains after the War of Wrath.
- House of the Lonely Mountain - The house associated with Erebor, home of Thorin Oakenshield.
- House of the Firebeards - Known for their fiery temper and craftsmanship.
- House of the Longbeards - A major clan that includes many notable dwarves, including Gimli.
- Germanic Folklore: (no specific group, primarily referencing the 7 of German fairy tale Snow White.)
- Disney’s "The Hobbit":
- Thorin Oakenshield - The leader of the dwarves and heir to the throne of Erebor.
- Balin - The wise and elder dwarf, known for his leadership and experience.
- Dwalin - Balin's brother, a fierce warrior with a strong sense of loyalty.
- Fili - The younger brother of Kili, known for his bravery and skill in battle.
- Kili - Fili's brother, adventurous and charming, with a keen eye for danger.
- Gloin - A stout dwarf, known for his practical nature and later appears in "The Lord of the Rings."
- Oin - Gloin's brother, skilled in healing and often carries a medical kit.
- German Fairy Tales: (no specific group, primarily referencing the 7 of German fairy tale Snow White.)
- Folklore Worldwide: ("7" dwarves idea is mainly associated with Western culture; primarily referencing the 7 of German fairy tale Snow White.)
- Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs: (7 dwarfs names)
- 7 different types of angles that are commonly recognized: (There actually multiple other types: Types of Angles)
- Acute Angle
- Right Angle
- Obtuse Angle
- Straight Angle
- Reflex Angle
- Complementary Angles
- Supplementary Angles
- 7 great sages or rishis in ancient India:
- Marichi
- Atri
- Angiras
- Pulastya
- Pulaha
- Kratu
- Vashishtha
- G7 refers to the Group of Seven, an international economic organization comprised of seven major advanced economies:
- Canada
- France
- Germany
- Italy
- Japan
- United Kingdom
- United States
- 7 Sisters Cliffs along the English Channel in Southern England: (Names of the 7 sisters):
- Haven Brow
- Short Brow
- Rough Brow
- Brass Point
- Flat Hill
- Bailey’s Hill
- Went Hill
- 7 Indian Chakras
- Root Chakra (Muladhara)
- Sacral Chakra (Swadhisthana)
- Solar Plexus Chakra (Manipura)
- Heart Chakra (Anahata)
- Throat Chakra (Vishuddha)
- Third Eye Chakra (Ajna)
- Crown Chakra (Sahasrara)
- Seven Samurai (Motion picture):
- Kambei Shimada - The wise leader and strategist.
- Gorobei Katayama - The skilled archer and second-in-command.
- Shichiroji - A loyal and experienced swordsman.
- Katsushiro Okamoto - The young and idealistic samurai.
- Heihachi Hayakawa - The cheerful and light-hearted fighter.
- Kyuzo - The master swordsman known for his exceptional skill.
- Kikuchiyo - The boisterous and passionate warrior with a complex background.
- 7 occurring in mathematical concepts or properties:
- Heptagon- A heptagon is a polygon with seven sides and seven angles.
- Seven Bridges of Königsberg Problem
- Seven Colors Theorem, also known as the Heawood Conjecture.
- Seven Circles Theorem- states that given any configuration of circles in the plane, at most seven of the circles can be tangent to each other.
- 7 Crystal Systems - In crystallography, there are seven distinct crystal systems that describe the different ways in which atoms can be arranged in a three-dimensional lattice.
- 7 Segment Display- A common arrangement of segments used to display numerals on digital clocks and electronic devices.
- 7 book series or sets that come in 7 volumes:
- The Chronicles of Narnia, by C.S. Lewis.
- Harry Potter- The main series consists of seven books by J.K. Rowling, each corresponding to a year of Harry’s education at Hogwarts School of Witchcraft and Wizardry.
- "The Clifton Chronicles" is a series of of seven historical fiction novels written by British author Jeffrey Archer.
- "The Incarnations of Immortality" is a series of fantasy novels written by American author Piers Anthony involving the various roles and responsibilities of powerful beings who take on the mantles of Death, Time, Fate, War, Nature, Evil, and Good.
Yep, I too would view the number 7 as being more significant if it were offered in a more comprehensive way than those who simply provide a handful of examples from different cultures from different peoples related to superstition and cultural traditions.
Likewise for the number "2" and its multiple referencing in biology. A closer examination reveals it to frequently be a part of a 3-part 1-2-3 developmental sequence or displayed expression.
The "three" expression in one or another form (triad, triangle, triunity, triple, ternary, trinary, etc...) does not belong to any single subject. For example, it is not a sacred number, though it is called such by some religious perspective. Nor is it a value evincing great power as described by some steeped deeply in the arts of mysticism.
Neither is the "three" owned by Fairy tales, Numerology, Astrology, Music, Mathematics, nor Eastern philosophy. In short, millions of people have misinterpreted the recurrence of the pattern simply because their field of research has been too narrow, and they are more interested in confirmation of some former idea than altering their views to align with their findings. Far too often those expressing some value of "3", do so with the attempt to produce some financial gain, social position, or create some other point of distinction that they may profit off of by way of manipulating one or more others. In other words, multiple people sharpen their usage of the "three" as if it were a tool like some arrow head, spear head, sword, dagger or pointing stick.
However, my current point is that the human mind can not develop beyond the "three" unless it learns to cognitively count where it presently is. An analogy to be used comes from the studies of those involving the birth of the cardinal counting system one, two, three..., which we claim occurred in an ordinal manner of 1st, 2nd, 3rd... The phrase "one- two- many" can be used to describe humanity's fledgling attempts at playing with a counting system. The sequence is generally though to have occurred like this:
- The number "1", perhaps inscribed as a simple line in the dirt or some stone/shell to mimic the perception of acknowledging one item.
- Everything else was termed some language or gesture equivalent "many" (heap, much, pile, etc...)
- By way of further pairing, some symbolic reference to the quantity of "2" was established.
- Everything else was termed "many".
- Hence, at this point humanity had created the three-part ideology of counting with their language/symbol equivalent terms of "1- 2- Many".
The following image I put together is a humorous means of illustrating the development of a counting system amongst early humans. It's not meant to be taken literally, just an imaginative explanation to create some intellectual ambiance of consideration.
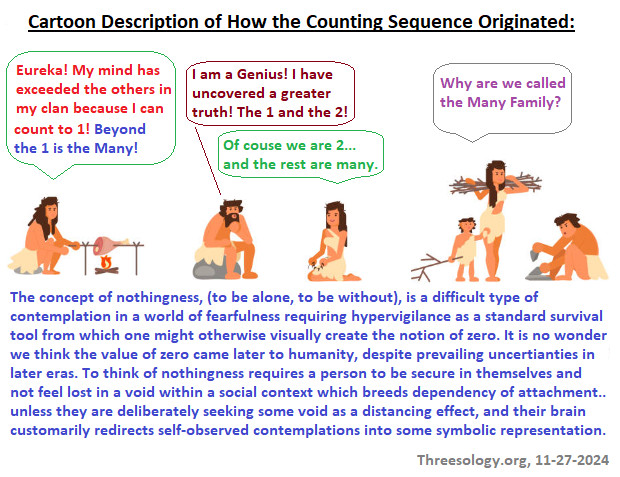
No, I am not saying the counting event took place in 3 steps. Humanity's system of basic counting could have taken centuries and developed by multiple people. I do not know how many stops, starts, reversals, or reinvention took place. Typically however, it appears that humanity adopted an affinity for numbers to deal with situations of commerce, that is... to barter for the trading of goods to the present day trading standards of using some form of currency, Solid (dollar bills/gold...)- Liquid (on paper)- Gaseous (such as stock market hypotheticals where the common person thinks that money simply vanished into thin air).
Yet, the counting method which I am trying to highlight is a different animal of conceptualization not involving immediate pecuniary rewards to be u sed as an incentive for further development of simple counting into an arithmetic that eventually ventures into its own geometry and higher mathematics.
Let me reiterate: Mathematics as we know it today arose from a (generally speaking) "1-2-Many" counting sequence based on pairing and associated with commerce (e.g. bartering/trading). This is not to say that the development was sequentially smooth without interruption or regression, nor that it didn't occur in multiple places with different stages of accomplishment. However, if we then let ourselves develop a counting system based on a trinary acknowledgment of the binary dependency which present mathematics has and instead use a multiplicity of three-patterned cognitive ideas to formulate a counting system based on a 3-part sharing associated at a distance from its application solely or mostly with no commercial interests, what is the shape such a mathematics will take?
In other words, the mathematics we have today developed by way of a one-to-one pairing system applied to commercial (trade/barter) interests out of which the pairing method was retained and evolved into a dynamically pervasive use of dualities/dichotomies either oppositionally and/or complementary applied as te basis for establishing mathematical proofs, protocols, rules, maxims and theorems. Proofing methods can be expressed in multiple ways, but the standard is to describe some model of duality. Take any random list of dualities and you can see the beginnings of a measure by which a proof can be originated. Different subjects will use their own vocabularies, yet all of them read like some alternatively described composite exercise of yin and yang polarizations/complements-compliments:
- direct/indirect proofing
- selective/grouped divisions
- induction/deduction
- congruous (congruity)/incongruous incongruity)
- construction/deconstruction
- intimation/exclamation
- mentally exercised hypothesis/experimentally exercise hypothesis
- question/exclamation
- variable/constant
- left side of equation/right side of equation
- solid-concrete/fluidic-gaseous
- axiom-truism (accepted as true without proof)/falsism (established as wrong-or a lie with proof)
- presumption/acceptance
- presumed hypotheticals/presumed facts
- proposition/opposition
- adopt/forego
- proposition/supposition
- proposition/agreement
- singular/collective
- Proofing by way of contradiction
- contradiction/confirmation
While some Mathematicians have attempted such a path, they are doing so from an unrecognized reliance of dualties and an appreciable ignorance about pattern-of-three formulations as a cognitive exercise of a fledgling counting system. While many a Mathematician (steeped deeply in a history of learning mathematics in the arena were dichotomous orientations reign) might call a list of threes an exercise in numerology, it can be seen as a rudimentary model of counting cognitive expressions, much like hearing a child repeating their numbers and letters as not only as a memorization technique, but as a stepwise activity to acquire greater proficiency of this type of thinking and its possible applications. Like early mathematics where different and more complex associations were made along with different applications, so too is the present rudimentary activity of listing a compilation of "threes" into various categories... just like early mathematics and writing skills require.
By developing a list of threes which influences others to think of other patterns, we begin to adopt a behavior for collecting lists of patterns which have become enumerated. We do not do this effectively by relying on models of thinking about numbers from traditional Mathematics nor Numerology or Astrology. Such lists help us to realize that there are only a few patterns that are widely recurring as defined by the examples from multiple subjects. Whereas present Mathematics got its origination from a binary model aligned with the communication of intent for commercial activities, the New Mathematics derives its orientation from trinary model of observing the deficiency of a binary upbringing so as to better communicate the language of cognitive perceptions.
In such a development, we need to identify the originations of not only all ideation, but those both specifically and related to some "three" value. Hence we need to look at the development of life and its precursors.
Let me now continue with the list of threes:
- 3-to-1 types of main logical reasoning:
- Informal logic is what's typically used in daily reasoning and arguments.
- Formal logic uses deductive reasoning and the premises must be true.
- Symbolic logic deals with how symbols relate to each other.
- Mathematical Logic- you apply formal logic to math.
-
3 Main types of Reasoning:
- Deductive reasoning: [conclusion guaranteed]; Deductive reasoning starts with the assertion of a general rule and proceeds from there to a guaranteed specific conclusion.
- Inductive reasoning: [conclusion merely likely]; Inductive reasoning begins with observations that are specific and limited in scope, and proceeds to a generalized conclusion that is likely, but not certain, in light of accumulated evidence.
- Abductive reasoning: [taking your best shot]; Abductive reasoning typically begins with an incomplete set of observations and proceeds to the likeliest possible explanation for the set. Abductive reasoning yields the kind of daily decision-making that does its best with the information at hand, which often is incomplete.
- 3 parts to syllogistic logic (I refer to it as "sillygistic" because many of the examples are quite silly.)
- 3-to-1 ratio of Rene Descartes' rules for the direction
of the mind(Supposedly corresponding to a direct application of Mathematical Procedures.):
- Accept nothing as true that is not self-evident.
- Divide problems into their simplest parts.
- Solve problems by proceeding from simple to complex.
- Recheck the reasoning.
Date of Origination: Tuesday, June 1st, 2025... 7:00 AM
Initial Posting Date: Saturday, August 10th, 2025... 1:24 AM